OpenShift Regional Disaster Recovery with Advanced Cluster Management
- 1. Overview
- 2. Deploy and Configure ACM for Multisite connectivity
- 3. OpenShift Data Foundation Installation
- 4. Install ODF Multicluster Orchestrator Operator on Hub cluster
- 5. Configure SSL access between S3 endpoints
- 6. Enabling Multicluster Web Console
- 7. Create Data Policy on Hub cluster
- 8. Create Sample Application for DR testing
- 9. Application Failover between managed clusters
- 10. Application Failback between managed clusters
1. Overview
The intent of this guide is to detail the steps and commands necessary to be able to failover an application from one OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) cluster to another and then failback the same application to the original primary cluster. In this case the OCP clusters will be created or imported using Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management or RHACM.
This is a general overview of the steps required to configure and execute OpenShift Disaster Recovery (ODR) capabilities using OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF) v4.11 and RHACM v2.5 across two distinct OCP clusters separated by distance. In addition to these two cluster called managed clusters, there is currently a requirement to have a third OCP cluster that will be the Advanced Cluster Management (ACM) hub cluster.
These steps are considered Tech Preview in ODF 4.11 and are provided for POC (Proof of Concept) purposes. OpenShift Regional Disaster Recovery will be supported for production usage in a future ODF release.
|
-
Install the ACM operator on the hub cluster.
After creating the OCP hub cluster, install from OperatorHub the ACM operator. After the operator and associated pods are running, create the MultiClusterHub resource. -
Create or import managed OCP clusters into ACM hub.
Import or create the two managed clusters with adequate resources for ODF (compute nodes, memory, cpu) using the RHACM console. -
Ensure clusters have unique private network address ranges.
Ensure the primary and secondary OCP clusters have unique private network address ranges. -
Connect the private networks using Submariner add-ons.
Connect the managed OCP private networks (cluster and service) using the RHACM Submariner add-ons. -
Install ODF 4.10 on managed clusters.
Install ODF 4.10 on primary and secondary OCP managed clusters and validate deployment. -
Install ODF Multicluster Orchestrator on the ACM hub cluster.
Install from OperatorHub on the ACM hub cluster the ODF Multicluster Orchestrator. The OpenShift DR Hub operator will also be installed. -
Configure SSL access between S3 endpoints
If managed OpenShift clusters are not using valid certificates this step must be done by creating a new user-ca-bundle ConfigMap that contains the certs. -
Enable Multicluster Web Console.
This is a new Tech Preview capability that is required before creating a DRPolicy. It is only needed on the Hub cluster where ACM resides. -
Create one or more DRPolicy
Use the All Clusters Data Services UI to create DRPolicy by selecting the two managed clusters the policy will apply to. -
Validate OpenShift DR Cluster operators are installed.
Once the first DRPolicy is created this will trigger the DR Cluster operators to be created on the two managed clusters selected in the UI. -
Create the Sample Application using ACM console.
Use the sample app example from github.com/RamenDR/ocm-ramen-samples to create a busybox deployment for failover and failback testing. -
Validate Sample Application deployment.
Using CLI commands on both managed clusters validate that the application is running. -
Apply DRPolicy to Sample Application.
Use the All Clusters Data Services UI to apply the new DRPolicy to the Sample Application. Once applied a DRPlacementControl resource will be created in the application namespace on the Hub cluster. -
Failover Sample Application to secondary managed cluster.
Modify the application DRPlacementControl resource on the Hub Cluster, add the action of Failover and specify the failoverCluster to trigger the failover. -
Failback Sample Application to primary managed cluster.
Modify the application DRPlacementControl resource on the Hub Cluster and change the action to Relocate to trigger a failback to the preferredCluster.
2. Deploy and Configure ACM for Multisite connectivity
This installation method requires you have three OpenShift clusters that have network reachability between them. For the purposes of this document we will use this reference for the clusters:
-
Hub cluster is where ACM, ODF Multisite-orchestrator and ODR Hub controllers are installed.
-
Primary managed cluster is where ODF, ODR Cluster controller, and Applications are installed.
-
Secondary managed cluster is where ODF, ODR Cluster controller, and Applications are installed.
2.1. Install ACM and MultiClusterHub
Find ACM in OperatorHub on the Hub cluster and follow instructions to install this operator.

Verify that the operator was successfully installed and that the MultiClusterHub is ready to be installed.
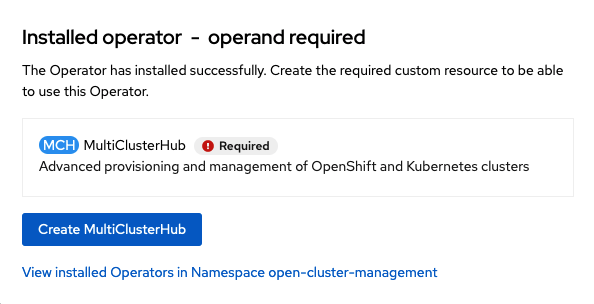
Select MultiClusterHub and use either Form view or YAML view to configure the deployment and select Create.
Most MultiClusterHub deployments can use default settings in the Form view.
|
Once the deployment is complete you can logon to the ACM console using your OpenShift credentials.
First, find the Route that has been created for the ACM console:
oc get route multicloud-console -n open-cluster-management -o jsonpath --template="https://{.spec.host}/multicloud/clusters{'\n'}"This will return a route similar to this one.
https://multicloud-console.apps.bos3.example.com/multicloud/clustersAfter logging in you should see your local cluster imported.
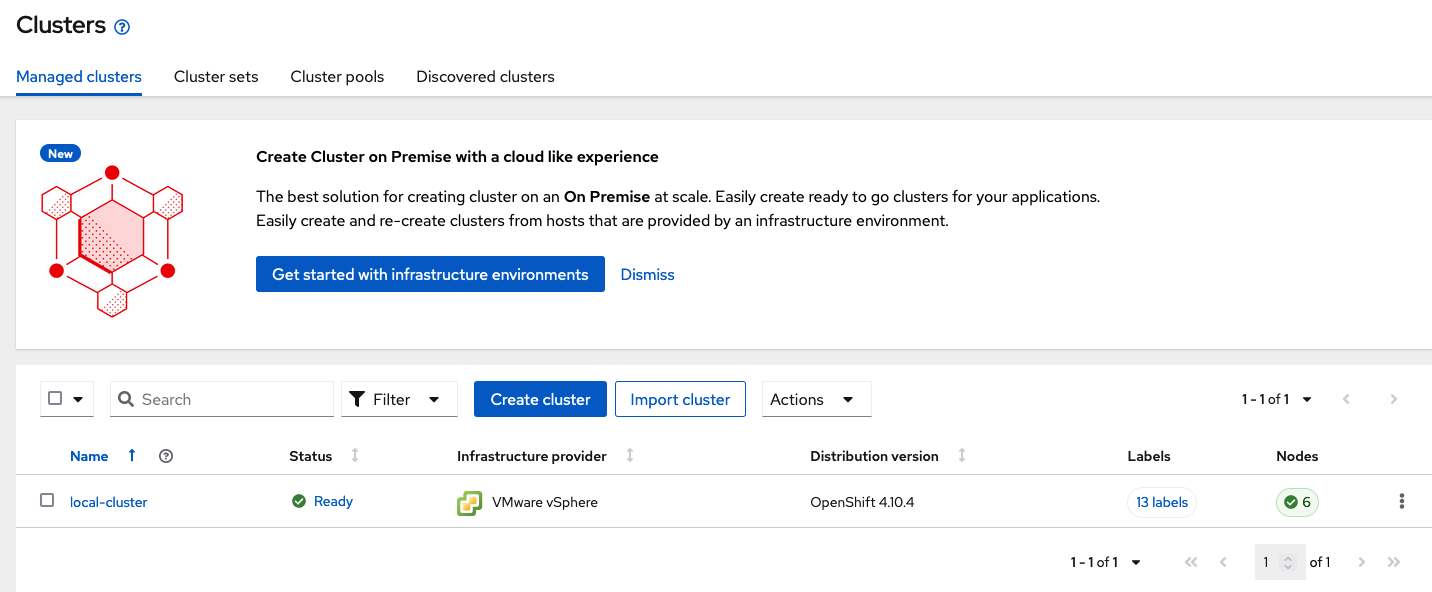
2.2. Import or Create Managed clusters
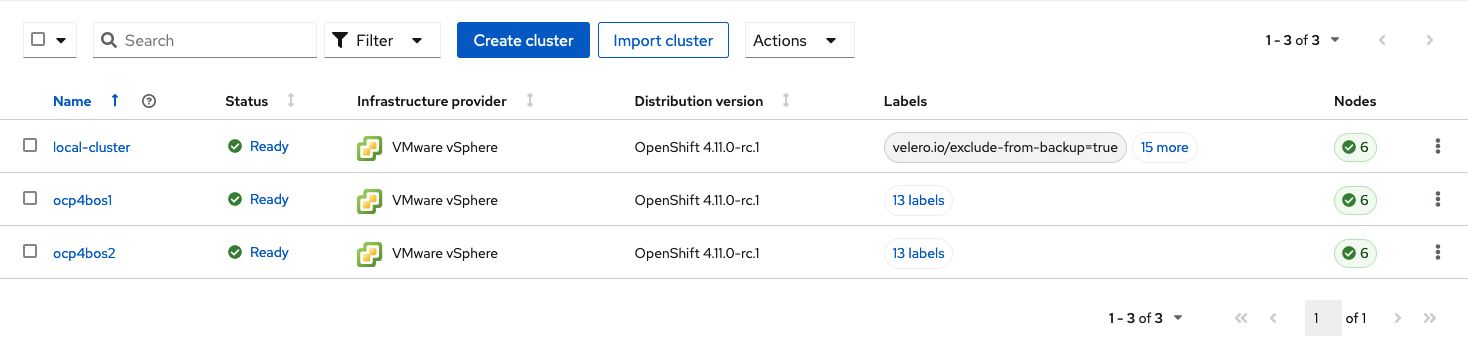
Now that ACM is installed on the Hub cluster it is time to either create or import the Primary managed cluster and the Secondary managed cluster. You should see selections (as in above diagram) for Create cluster and Import cluster. Chose the selection appropriate for your environment. After the managed clusters are successfully created or imported you should see something similar to below.
2.3. Verify Managed clusters have non-overlapping networks
In order to connect the OpenShift cluster and service networks using the Submariner add-ons, it is necessary to validate the two clusters have non-overlapping networks. This can be done by running the following command for each of the managed clusters.
oc get networks.config.openshift.io cluster -o json | jq .spec{
"clusterNetwork": [
{
"cidr": "10.5.0.0/16",
"hostPrefix": 23
}
],
"externalIP": {
"policy": {}
},
"networkType": "OpenShiftSDN",
"serviceNetwork": [
"10.15.0.0/16"
]
}{
"clusterNetwork": [
{
"cidr": "10.6.0.0/16",
"hostPrefix": 23
}
],
"externalIP": {
"policy": {}
},
"networkType": "OpenShiftSDN",
"serviceNetwork": [
"10.16.0.0/16"
]
}These outputs show that the two example managed clusters have non-overlapping clusterNetwork and serviceNetwork ranges so it is safe to proceed.
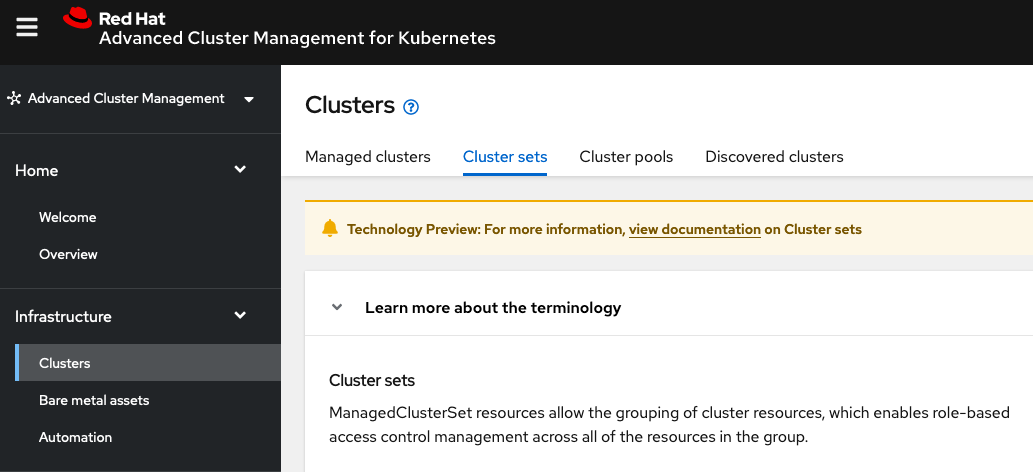
2.4. Connect the Managed clusters using Submariner add-ons
Now that we know the cluster and service networks have non-overlapping ranges, it is time to move on to installing the Submariner add-ons for each managed cluster. This is done by using the ACM console and Cluster sets.
Navigate to selection shown below and at the bottom of the same page, select Create cluster set.
Once the new Cluster set is created select Manage resource assignments.
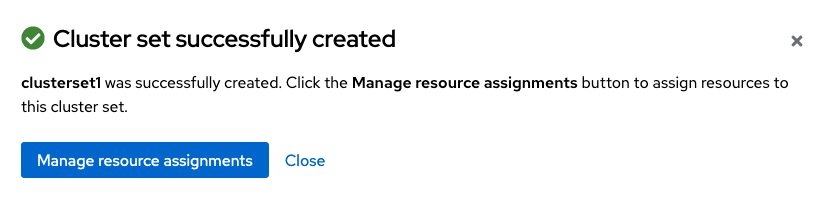
Follow the instructions and add the two managed clusters to the new Cluster set. Select Save and then navigate to Submariner add-ons.
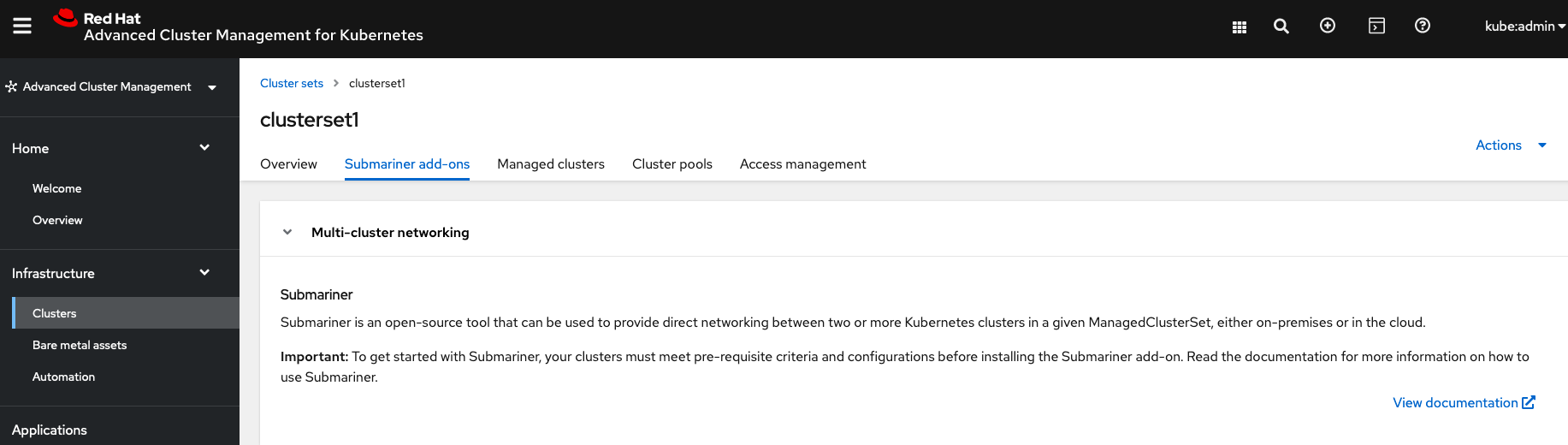
Select Install Submariner add-ons at the bottom of the page and add the two managed clusters. Click through the wizard selections and make changes as needed. After Review of your selections select Install.
Do not select Enable Globalnet because of overlapping cluster and service networks for the managed clusters. Using Globalnet is not supported with Regional Disaster Recovery currently. Ensure that cluster and service networks are non-overlapping before proceeding.
|
It can take more than 5 minutes for the Submariner add-ons installation to finish on both managed clusters. Resources are installed in the submariner-operator project.
|
A successful deployment will show Connection status and Agent status as Healthy.
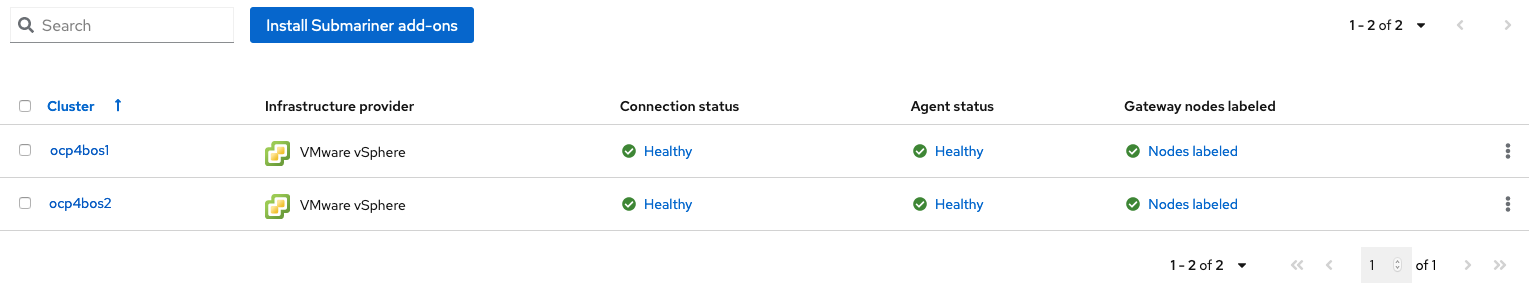
3. OpenShift Data Foundation Installation
In order to configure storage replication between the two OCP clusters OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF) must be installed first on each managed cluster. ODF deployment guides and instructions are specific to your infrastructure (i.e. AWS, VMware, BM, Azure, etc.). Install ODF version 4.11 on both OCP managed clusters.
You can validate the successful deployment of ODF on each managed OCP cluster with the following command:
oc get storagecluster -n openshift-storage ocs-storagecluster -o jsonpath='{.status.phase}{"\n"}'And for the Multi-Cluster Gateway (MCG):
oc get noobaa -n openshift-storage noobaa -o jsonpath='{.status.phase}{"\n"}'If the result is Ready for both queries on the Primary managed cluster and the Secondary managed cluster continue on to configuring mirroring.
| The successful installation of ODF can also be validated in the OCP Web Console by navigating to Storage and then Data Foundation. |
4. Install ODF Multicluster Orchestrator Operator on Hub cluster
On the Hub cluster navigate to OperatorHub and filter for ODF Multicluster Orchestrator. Follow instructions to Install the operator into the project openshift-operators. The ODF Multicluster Orchestrator also installs the Openshift DR Hub Operator on the ACM hub cluster as a dependency.
Check to see the operators Pod are in a Running state. The OpenShift DR Hub operator will be installed at the same time in openshift-operators.
oc get pods -n openshift-operatorsNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
odfmo-controller-manager-f6fc95f7f-7wtjl 1/1 Running 0 4m14s
ramen-hub-operator-85465bd487-7sl2k 2/2 Running 0 3m40s
odf-multicluster-console-76b88b444c-vl9s4 1/1 Running 0 3m50s5. Configure SSL access between S3 endpoints
These steps are necessary so that metadata can be stored on the alternate cluster in a Multi-Cloud Gateway (MCG) object bucket using a secure transport protocol and in addition the Hub cluster needs to verify access to the object buckets.
| If all of your OpenShift clusters are deployed using signed and valid set of certificates for your environment then this section can be skipped. |
Extract the ingress certificate for the Primary managed cluster and save the output to primary.crt.
oc get cm default-ingress-cert -n openshift-config-managed -o jsonpath="{['data']['ca-bundle\.crt']}" > primary.crtExtract the ingress certificate for the Secondary managed cluster and save the output to secondary.crt.
oc get cm default-ingress-cert -n openshift-config-managed -o jsonpath="{['data']['ca-bundle\.crt']}" > secondary.crtCreate a new YAML file cm-clusters-crt.yaml to hold the certificate bundle for both the Primary managed cluster and the Secondary managed cluster.
| There could be more or less than three certificates for each cluster as shown in this example file. |
apiVersion: v1
data:
ca-bundle.crt: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
<copy contents of cert1 from primary.crt here>
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
<copy contents of cert2 from primary.crt here>
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
<copy contents of cert3 primary.crt here>
-----END CERTIFICATE----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
<copy contents of cert1 from secondary.crt here>
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
<copy contents of cert2 from secondary.crt here>
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
<copy contents of cert3 from secondary.crt here>
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: user-ca-bundle
namespace: openshift-configThis ConfigMap needs to be created on the Primary managed cluster, Secondary managed cluster, and the Hub cluster.
oc create -f cm-clusters-crt.yamlconfigmap/user-ca-bundle created
The Hub cluster needs to verify access to the object buckets using the DRPolicy resource. Therefore the same ConfigMap, cm-clusters-crt.yaml, needs to be created on the Hub cluster.
|
After all the user-ca-bundle ConfigMaps are created, the default Proxy cluster resource needs to be modified.
Patch the default Proxy resource on the Primary managed cluster, Secondary managed cluster, and the Hub cluster.
oc patch proxy cluster --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"trustedCA":{"name":"user-ca-bundle"}}}'proxy.config.openshift.io/cluster patched6. Enabling Multicluster Web Console
This is a new capability that is required before creating a Data Policy or DRPolicy. It is only needed on the Hub cluster and RHACM 2.5 must be installed.
| Multicluster console is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process. |
Enable the feature gate by navigating from Administration → Cluster Settings → Configuration → FeatureGate, and edit the YAML template as follows:
[...]
spec:
featureSet: TechPreviewNoUpgradeClick Save to enable the multicluster console for all clusters in the RHACM console.
| Do not set this feature gate on production clusters. You will not be able to upgrade your cluster after applying the feature gate, and it cannot be undone. |
7. Create Data Policy on Hub cluster
Regional Disaster Recovery uses the DRPolicy resources on the Hub cluster to failover and relocate workloads across managed clusters. A DRPolicy requires a set of two DRClusters or peer clusters with ODF version 4.11 installed. The ODF MultiCluster Orchestrator Operator facilitates the creation of each DRPolicy and the corresponding DRClusters through the Multicluster Web console.
On the Hub cluster navigate to All Clusters. Then navigate to Data policies under Data services menu. If this your first DRPolicy created you will see Create DRpolicy at the bottom of the page.
Make sure to login to all clusters from the Multicluster Web console. The clusters will be directly below All Clusters.
|
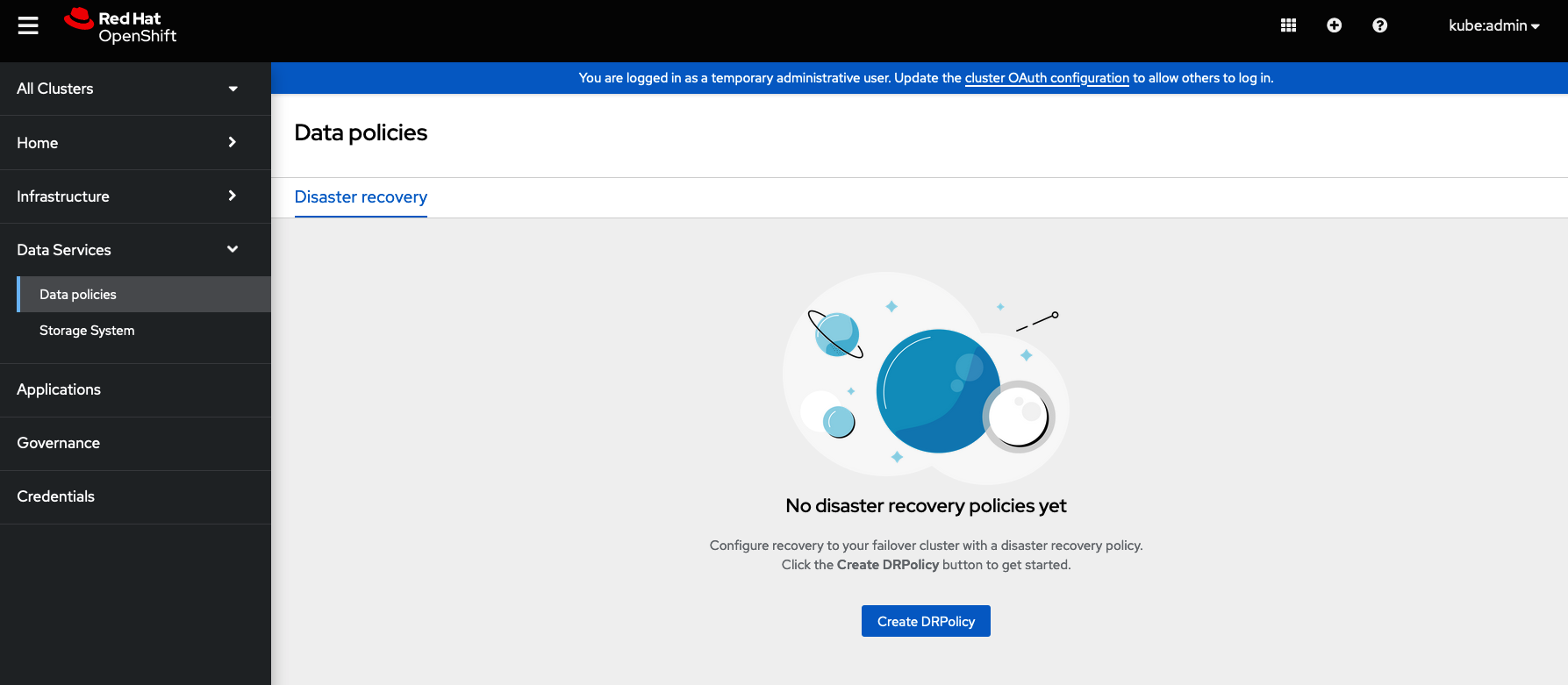
Click on Create DRPolicy. Select the clusters presented from the list of managed clusters that you would like to participate in the DRPolicy and give the policy a unique name (i.e., ocp4bos1-ocp4bos2-5m).
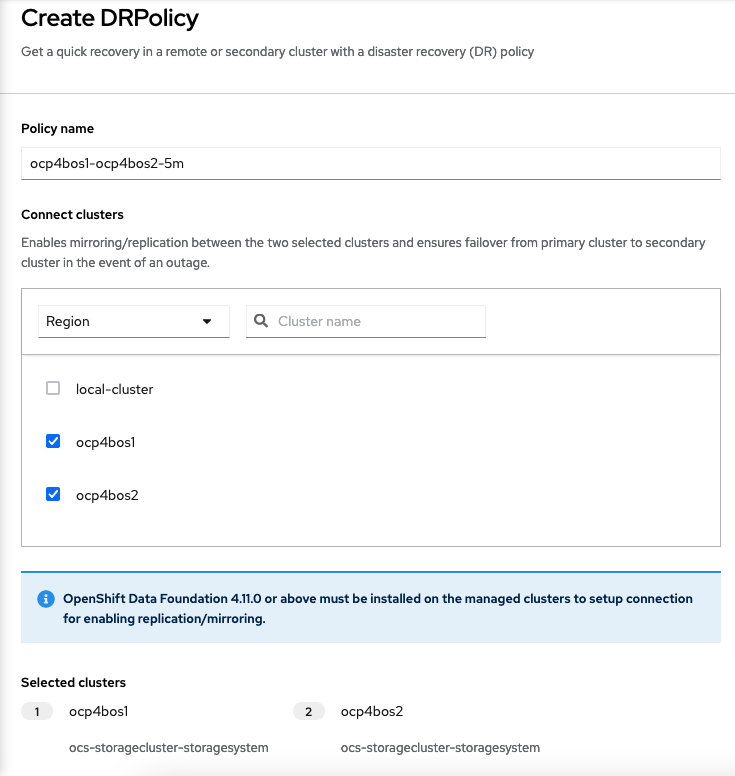
The greyed out dropdown option for Replication policy will automatically be selected as async based on the OpenShift clusters selected and a Sync schedule will be available. Select the replication interval for this DRPolicy and then select Create.
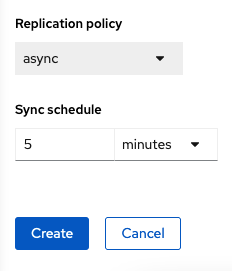
| For every desired replication interval a new DRPolicy needs to be created with a unique name (i.e., ocp4bos1-ocp4bos2-10m). The same clusters could be selected but the Sync schedule would be configured with a different replication interval in minutes. The minimum is one minute. |
This should create the two DRCluster resources and also the DRPolicy on the Hub cluster. In addition, when the initial DRPolicy is created the following will happen:
-
Create a bootstrap token and exchanges this token between the managed clusters.
-
Enable mirroring for the default
CephBlockPoolon each managed clusters. -
Create a VolumeReplicationClass on the Primary managed cluster and the Secondary managed cluster for the replication interval in the DRPolicy.
-
An object bucket created (using MCG) on each managed cluster for storing PVC and PV metadata.
-
A Secret created in the
openshift-operatorsproject on the Hub cluster for each new object bucket that has the base64 encoded access keys. -
The
ramen-hub-operator-configConfigMap on the Hub cluster is modified withs3StoreProfilesentries. -
The
OpenShift DR Clusteroperator will be deployed on each managed cluster in theopenshift-dr-systemproject. -
The object buckets Secrets on the Hub cluster in the project
openshift-operatorswill be copied to the managed clusters in theopenshift-dr-systemproject. -
The
s3StoreProfilesentries will be copied to the managed clusters and used to modify theramen-dr-cluster-operator-configConfigMap in theopenshift-dr-systemproject.
To validate that the DRPolicy is created successfully run this command on the Hub cluster for the each DRPolicy resource created.
Replace <drpolicy_name> with your unique name.
|
oc get drpolicy <drpolicy_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions[].reason}{"\n"}'SucceededTo validate object bucket access from the Hub cluster to both the Primary managed cluster and the Secondary managed cluster first get the names of the DRClusters on the Hub cluster.
oc get drclustersNAME AGE
ocp4bos1 4m42s
ocp4bos2 4m42sNow test S3 access to each bucket created on each managed cluster using this DRCluster validation command.
Replace <drcluster_name> with your unique name.
|
oc get drcluster <drcluster_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions[2].reason}{"\n"}'Succeeded| Make sure to run command for both DRClusters on the Hub cluster. |
To validate that the OpenShift DR Cluster operator installation was successful on the Primary managed cluster and the Secondary managed cluster do the following command:
oc get csv,pod -n openshift-dr-systemNAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
clusterserviceversion.operators.coreos.com/odr-cluster-operator.v4.11.0 Openshift DR Cluster Operator 4.11.0 Succeeded
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ramen-dr-cluster-operator-5564f9d669-f6lbc 2/2 Running 0 5m32sYou can also go to OperatorHub on each of the managed clusters and look to see the OpenShift DR Cluster Operator is installed.
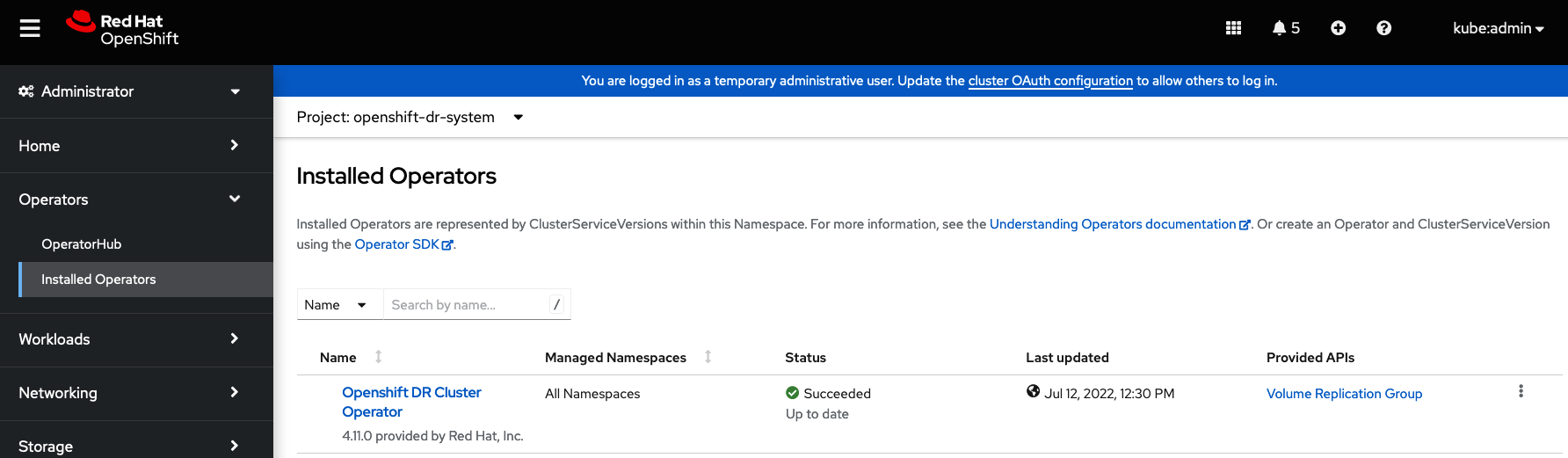
Validate the status of the ODF mirroring daemon health on the Primary managed cluster and the Secondary managed cluster.
oc get cephblockpool ocs-storagecluster-cephblockpool -n openshift-storage -o jsonpath='{.status.mirroringStatus.summary}{"\n"}'{"daemon_health":"OK","health":"OK","image_health":"OK","states":{}}
It could take up to 10 minutes for the daemon_health and health to go from Warning to OK. If the status does not become OK eventually then use the ACM console to verify that the Submariner connection between managed clusters is still in a healthy state. Do not proceed until all values are OK.
|
8. Create Sample Application for DR testing
In order to test failover from the Primary managed cluster to the Secondary managed cluster and back again we need a simple application. The sample application used for this example with be busybox.
8.1. Creating Sample Application using ACM console
Start by loggin into the ACM console using your OpenShift credentials if not already logged in.
oc get route multicloud-console -n open-cluster-management -o jsonpath --template="https://{.spec.host}/multicloud/applications{'\n'}"This will return a route similar to this one.
https://multicloud-console.apps.bos3.example.com/multicloud/applicationsAfter logging in select Create application in the top right and choose Subscription.
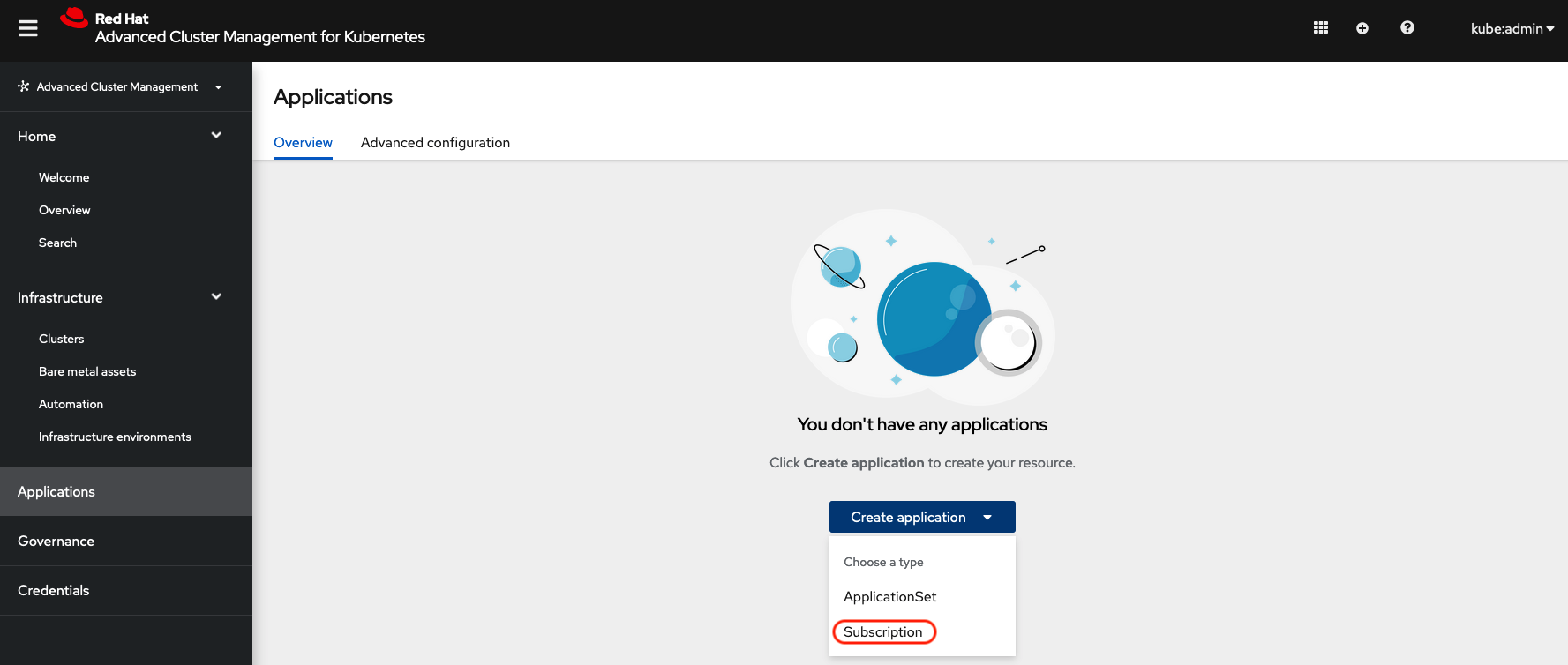
Fill out the top of the Create an application form as shown below and select repository type Git.
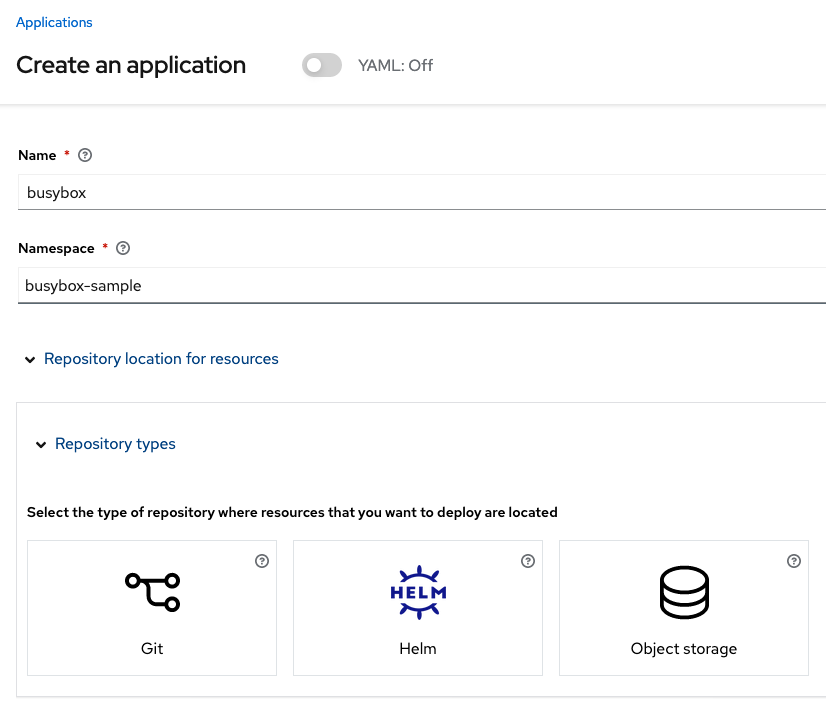
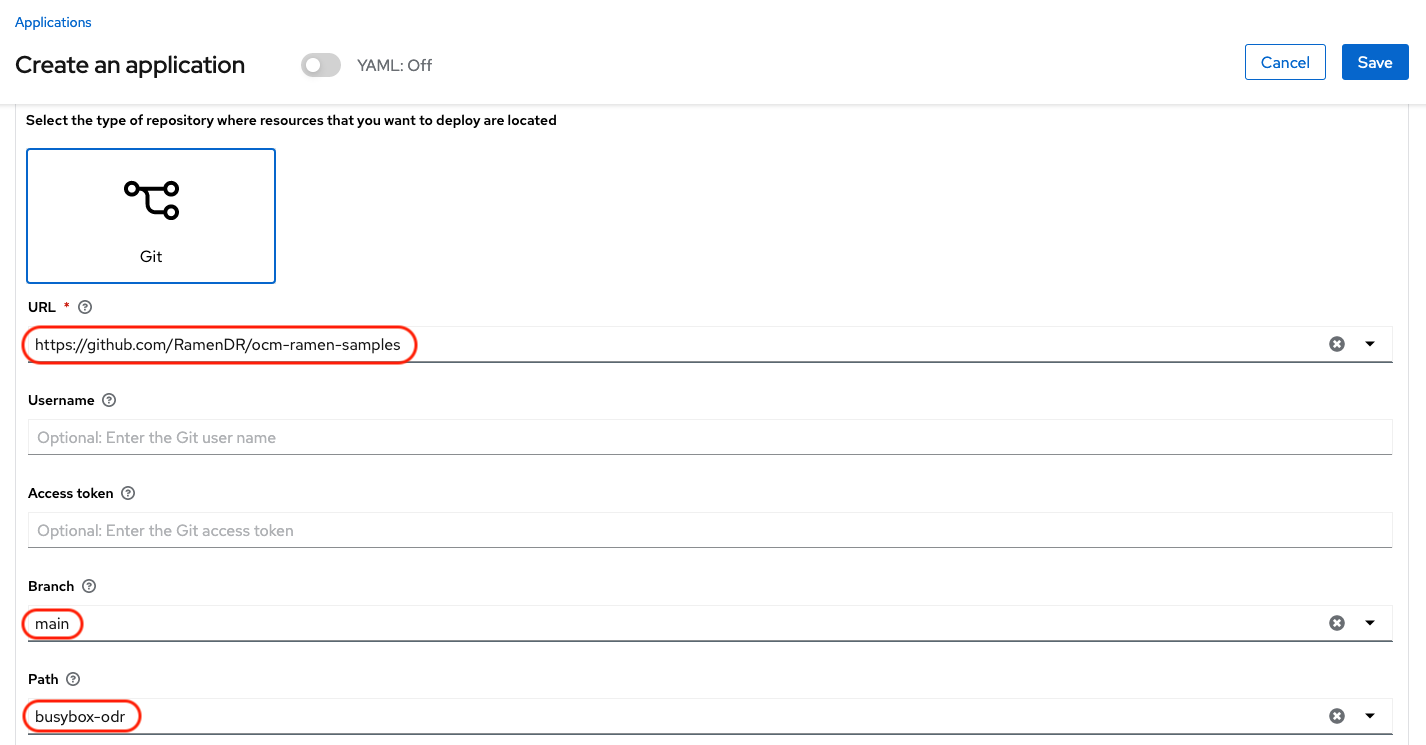
The next section to fill out is below the Git box and is the repository URL for the sample application, the github branch and path to resources that will be created, the busybox Pod and PVC.
Sample application repository github.com/RamenDR/ocm-ramen-samples. Branch is main and path is busybox-odr.
|
Scroll down in the form until you see Deploy application resources only on clusters matching specified labels and then add a label for the Primary managed cluster name in RHACM cluster list view.
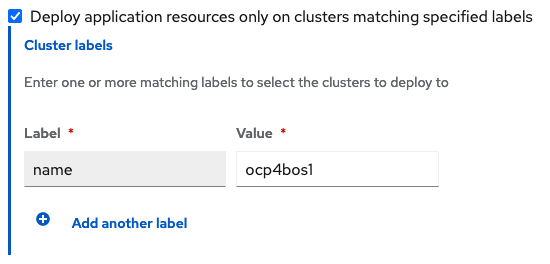
After adding the Label to identify the cluster, select Save in the upper right hand corner.
On the follow-on screen go to the Topology tab. You should see that there are all Green checkmarks on the application topology.
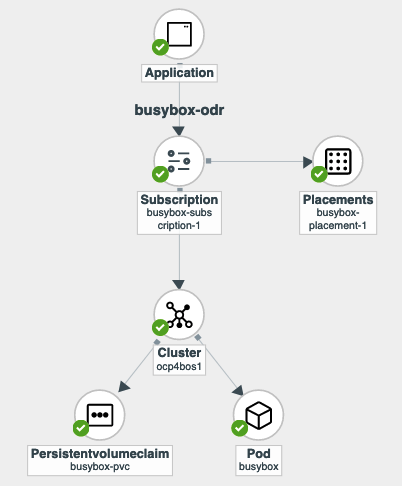
| To get more information click on any of the topology elements and a window will appear to right of the topology view. |
8.2. Validating Sample Application deployment
Now that the busybox application has been deployed to your Primary managed cluster the deployment can be validated.
Logon to your managed cluster where busybox was deployed by ACM. This is most likely your Primary managed cluster.
oc get pods,pvc -n busybox-sampleNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/busybox 1/1 Running 0 6m
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/busybox-pvc Bound pvc-a56c138a-a1a9-4465-927f-af02afbbff37 1Gi RWO ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd 6m8.3. Apply DRPolicy to Sample Application
On the Hub cluster go back to the Multicluster Web console and select All Clusters in the top right hand corner.
Make sure to login to all clusters from the Multicluster Web console. The clusters will be directly below All Clusters.
|
Navigate to Data Services and then choose Data policies. You should see the DRPolicy you created earlier in these instructions, section Create Data Policy on Hub cluster. At the far right of the DRPolicy select the vertical dots as shown below.
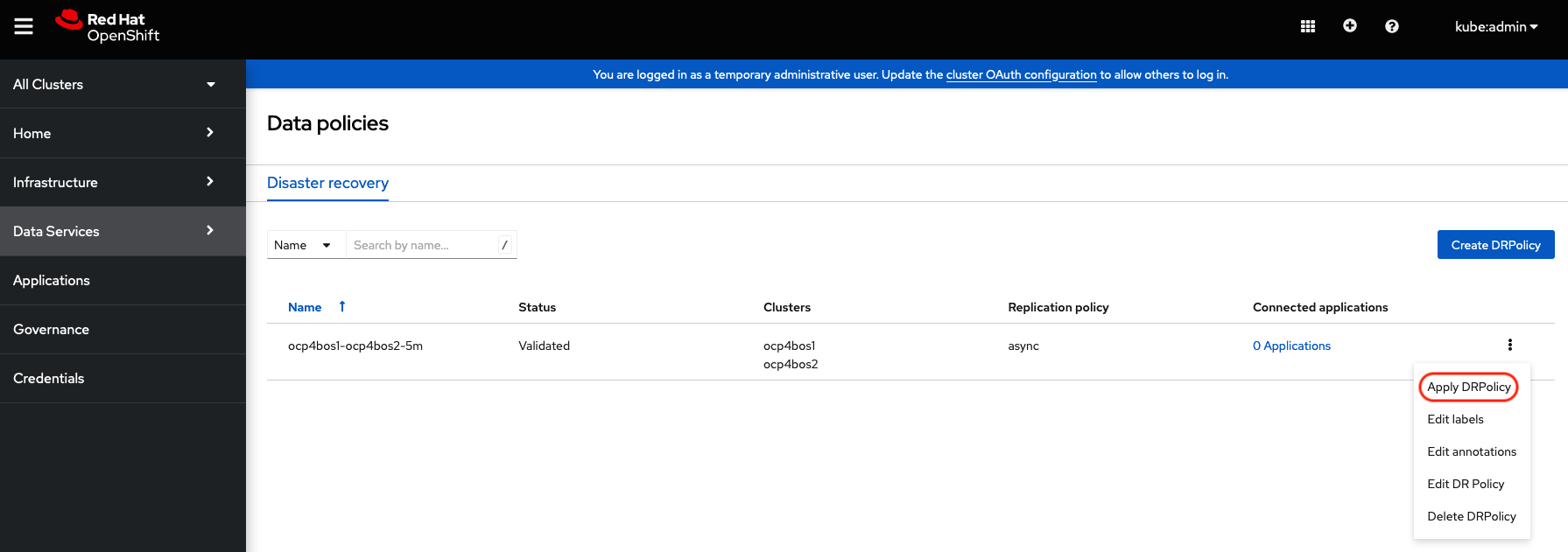
When the Apply DRPolicy box appears select busybox and then Apply.
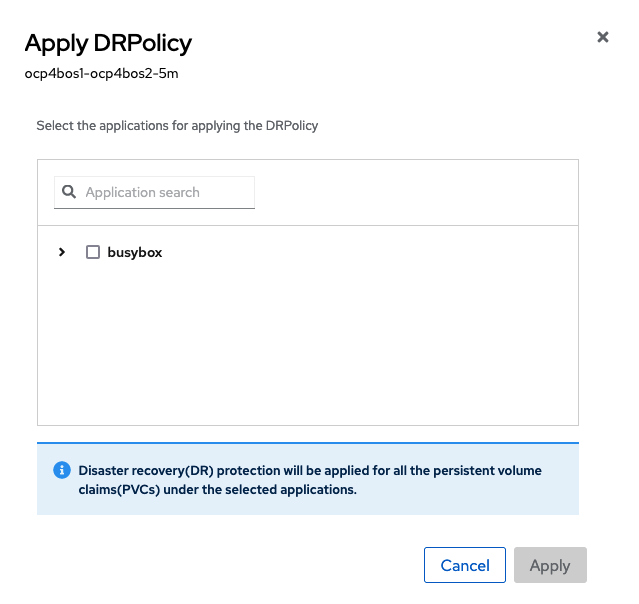
Validate that a DRPlacementControl or DRPC was created in the busybox-sample namespace on the Hub cluster. This resource is used for both failover and failback actions for this application.
oc get drpc -n busybox-sampleNAME AGE PREFERREDCLUSTER FAILOVERCLUSTER DESIREDSTATE CURRENTSTATE
busybox-placement-1-drpc 6m59s ocp4bos1 Deployed8.4. Deleting the Sample Application
Deleting the busybox application can be done using the ACM console. Navigate to Applications and then find the application to be deleted (busybox in this case).
| The instructions to delete the sample application should not be executed until the failover and failback (relocate) testing is completed and you want to remove this application from RHACM and from the managed clusters. |
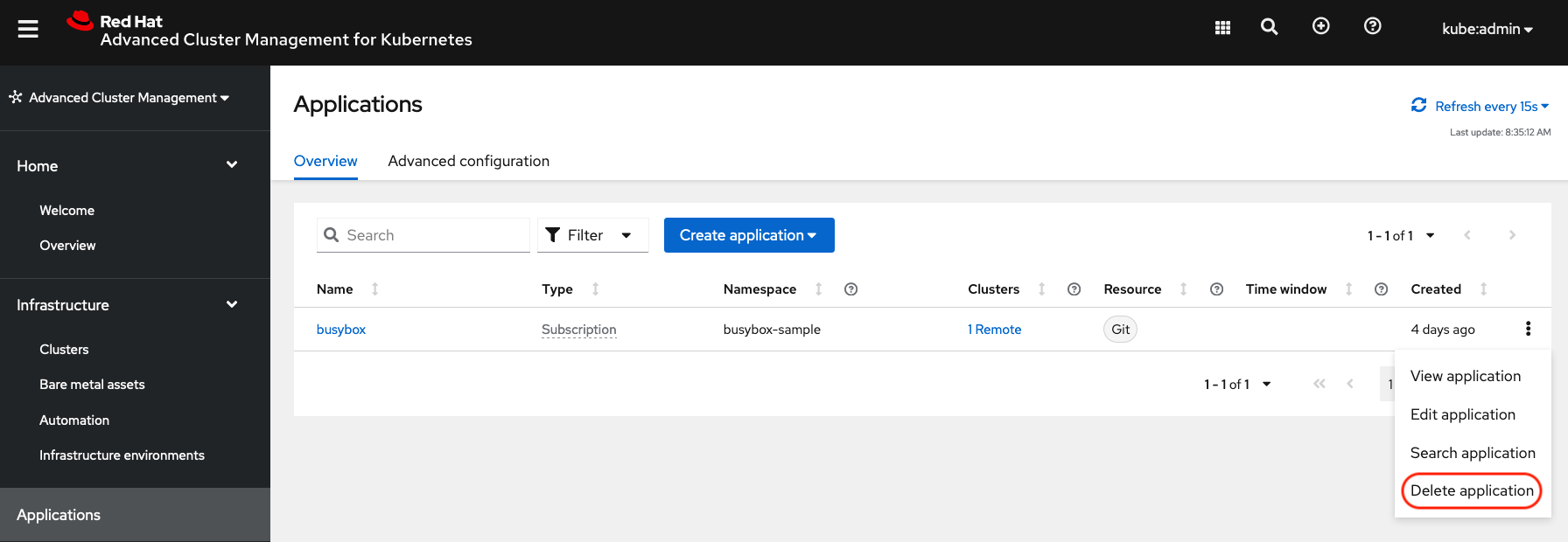
When Delete application is selected a new screen will appear asking if the application related resources should also be deleted. Make sure to check the box to delete the Subscription and PlacementRule.
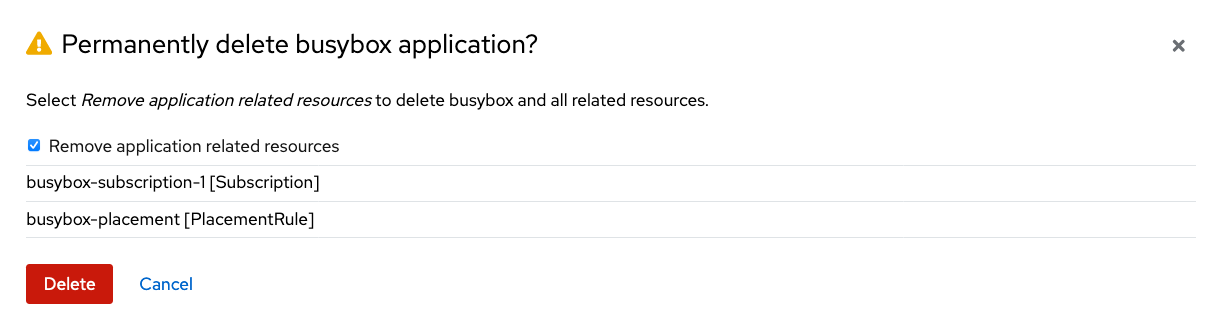
Select Delete in this screen. This will delete the busybox application on the Primary managed cluster (or whatever cluster the application was running on).
In addition to the resources deleted using the ACM console, the DRPlacementControl must also be deleted immediately after deleting the busybox application. Logon to the OpenShift Web console for the Hub cluster. Navigate to Installed Operators for the project busybox-sample. Choose OpenShift DR Hub Operator and the DRPlacementControl.
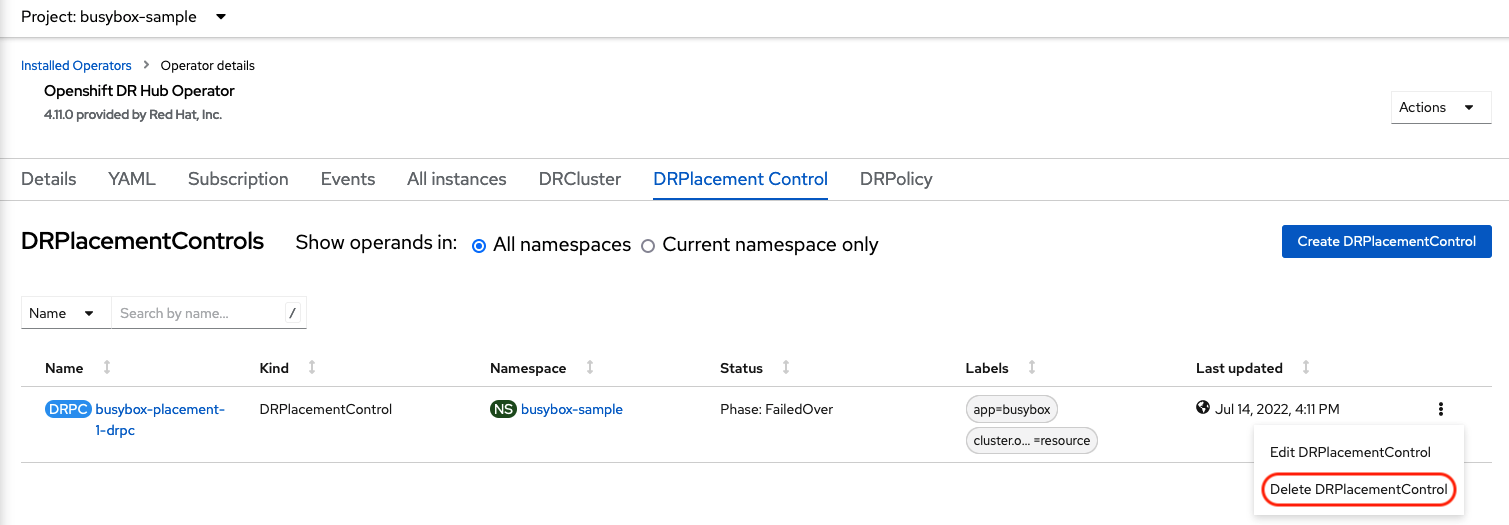
Select Delete DRPlacementControl.
If desired, the DRPlacementControl resource can also be deleted in the application namespace using CLI.
|
| This process can be used to delete any application with a DRPlacementControl resource. |
9. Application Failover between managed clusters
This section will detail how to failover the busybox sample application. The failover method for Metro Disaster Recovery is application based. Each application that is to be protected in this manner must have a corresponding DRPlacementControl in the application namespace as shown in the Apply DRPolicy to Sample Application section.
9.1. Modify DRPlacementControl to failover
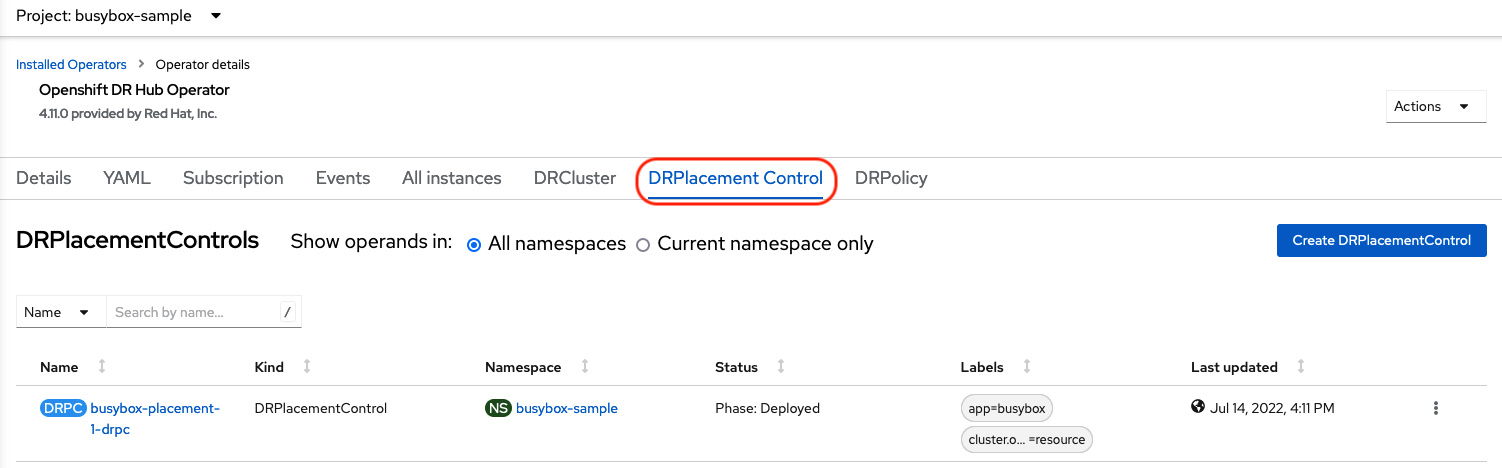
To failover requires modifying the DRPlacementControl YAML view. On the Hub cluster navigate to Installed Operators and then to Openshift DR Hub Operator. Select DRPlacementControl as show below.
Make sure to be in the busybox-sample namespace.
|
Select busybox-placement-1-drpc and then the YAML view. Add the action and failoverCluster as shown below. The failoverCluster should be the ACM cluster name for the Secondary managed cluster.
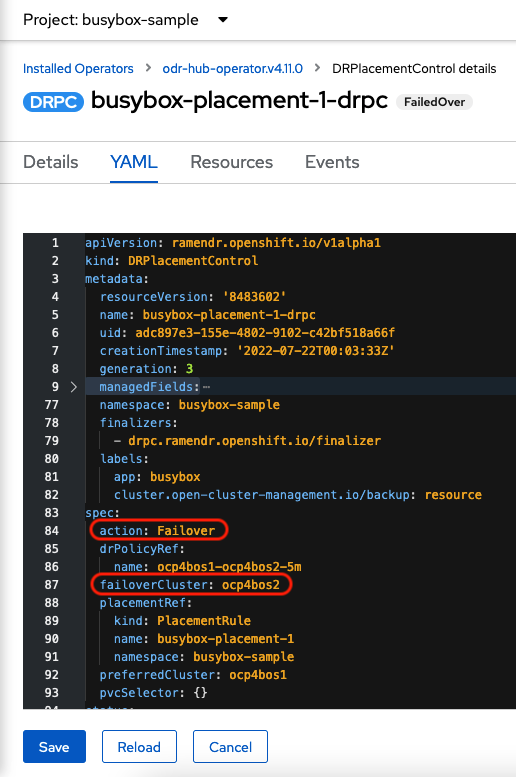
Select Save.
In the failoverCluster specified in the YAML file (i.e., ocp4bos2), see if the application busybox is now running in the Secondary managed cluster using the following command:
oc get pods,pvc -n busybox-sampleNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/busybox 1/1 Running 0 35s
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/busybox-pvc Bound pvc-79f2a74d-6e2c-48fb-9ed9-666b74cfa1bb 5Gi RWO ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd 35sNext, using the same command check if busybox is running in the Primary managed cluster. The busybox application should no longer be running on this managed cluster.
oc get pods,pvc -n busybox-sampleNo resources found in busybox-sample namespace.10. Application Failback between managed clusters
A failback operation is very similar to failover. The failback is application based and again uses the DRPlacementControl action value to trigger the failback. In this case the action is Relocate to the preferredCluster.
10.1. Modify DRPlacementControl to failback
To failback requires modifying the DRPlacementControl YAML view. On the Hub cluster navigate to Installed Operators and then to Openshift DR Hub Operator. Select DRPlacementControl as show below.
Make sure to be in the busybox-sample namespace.
|

Select busybox-placement-1-drpc and then the YAML form. Modify the action to Relocate as shown below.
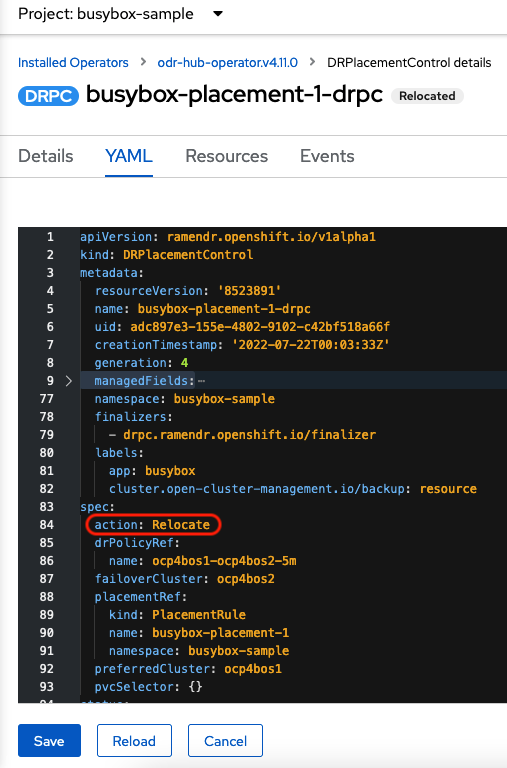
Select Save.
Check if the application busybox is now running in the Primary managed cluster using the following command. The failback is to the preferredCluster which should be where the application was running before the failover operation.
oc get pods,pvc -n busybox-sampleNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/busybox 1/1 Running 0 60s
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/busybox-pvc Bound pvc-79f2a74d-6e2c-48fb-9ed9-666b74cfa1bb 5Gi RWO ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd 61sNext, using the same command, check if busybox is running in the Secondary managed cluster. The busybox application should no longer be running on this managed cluster.
oc get pods,pvc -n busybox-sampleNo resources found in busybox-sample namespace.